We are here again with another interesting theme related to automobile technology in this edition. In case you are new here, we try to take up complicated technical aspects of automobile engineering and explain them to the readers in a simple manner so that you can understand the technology behind a ton of things in your car without the hassle of maneuvering through the complexities of concepts. This is what has encouraged us to dig for new and interesting topics and prepare articles for you. The topic for today is the types of engine layouts that are common in production cars. Let us get into the thick of it.
Also read: What are Intercoolers? What are their functions and working?

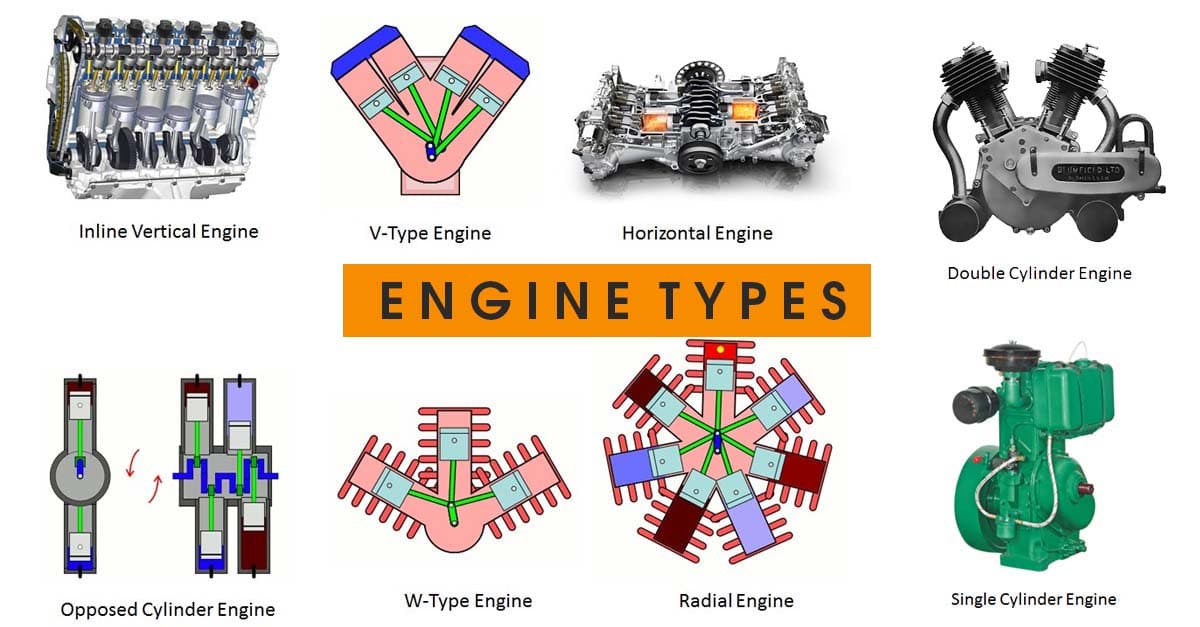
Types of Engine Layouts
While listening or reading the specifications list of any car, you must have heard the terms inline, V or VR, which are the most common engine configuration types for most automobiles around the world. Have you ever wondered what this could mean or what are the possible reasons for such configurations? Can’t we have a single master configuration that works for all cars? Well, the answer is not so simple. There are various kinds of cars out there with various requirements and environments. Not all cars serve the same purpose for everyone. Some people buy cars just for the purpose of mobility to move from one place to another. Other people are interested in getting the maximum performance out of their cars. Hence, they are looking for something sporty and fast. Other people want to have a comfortable ride and smooth operation to enjoy the luxury of a car. For all these scenarios, different types of engine layouts are suitable. Therefore, let us take a look at the different kinds of engine configurations and their characteristics.
Also read: How do Power and Torque overcome the Resistive Forces in a car?
Inline Engine
Undoubtedly the most common type of engine found in vehicles today is the inline engine. This refers to the fact that the cylinders of the engine are placed in one single line. There are various characteristics of such arrangements. This includes simple constructions, relatively balanced engine operation, easy maintenance and lower costs of manufacturing by being the most common engine types. The inline cylinder configuration can have any number of cylinders attached to it but normally you will find inline 1,2,3,4,5,6 cylinder engines mostly used in production cars. The inline cylinders require just a single/dual overhead camshaft, single crankshaft and connecting rod. That is the reason for the simplicity of these arrangements.
Also read: What is Engine Braking? How does Cooling System work?
For bikes, the most common type of engine layout is a single-cylinder layout. For some smaller cars, there are two or three cylinders used. Nowadays, the concept of downsizing is very prevalent which had made the turbo petrol inline 3 cylinder engines very common. This is also a perfect solution to tackle emissions and enhance performance with a smaller capacity engine. There may be certain vibrations attached to the inline 3 because of an odd number of cylinders that produce various forces. In the case of an inline 4 cylinder arrangement, the secondary forces from the moving of the pistons require an additional balancing shaft to counter the forces enabling a smooth operation of the engine.
As the number of cylinders keeps getting higher, the space consumed by the inline arrangement also increases and makes it a bit difficult to pack in the engine of the car. Therefore, inline 5, 6 and higher, are not very common these days.
Also read: Regular Fuel vs Premium Fuel – Should you use premium fuel in your car?
V Engines
When the number of cylinders increases, the V-type arrangement offers better benefits compared to an inline type. This essentially refers to two inline cylinder banks which are fixed at an angle which makes a V, hence, the name. These are way more compact than the inline type because of their shorter length. But at the same time, these are a bit wider. Overall, 6,8,10 or 12 cylinders are generally mounted in the cars with the help of the V-type arrangement. The V-type engines are very smooth and balanced which is an inherent property of such an arrangement. In most cars today, if the number of cylinders is more than 4, it will most likely be a V-type arrangement. The typical examples are V6, V8, V10 or V12. The inlet and exhaust arear are properly segregated in this type of arrangement because of the usage of two cylinder banks. The hot and cold areas are separated here.
Also read: How does OBD (On-Board Diagnostics) work?
VR Engines
VR type of engines was made popular largely by the Volkswagen group, which used this arrangement in a lot of their products. This is a very unique design in that it takes the best of both worlds. It has the characteristics of the V for the performance aspects and the smoothness of the inline which enables a more compact design. This enables the big VR6 engines to be able to fit in small cars as well. However, these days these kinds of engines are not very common.
Also read: What is engine knock? What are its consequences? How to prevent it?
W, H, U Engines
All these arrangements essentially represent the visual image they form when arranged in a certain way. A W-type arrangement represents 2 V-type setups that require a lot more components to operate. But for performance cars, more cylinders are needed and the cost is generally not an issue. Therefore, such kinds of arrangements are very much used in high-end luxury sports cars.
Also read: What are Catalytic Converters? How do they reduce pollution?
Rotary Engines
The rotary engines are truly a unique concept and have been made successful by the likes of Porsche. These are also called the Wankel Motors or Wankel Engines. The procedure is very different from that of a regular reciprocating piston-cylinder arrangement. There are far fewer moving components and the operation is extremely smooth. There is a curved triangular component, inside which there is a rotor fitted. This rotor is directly connected to the eccentric output shaft or the driving shaft. There are holes in the triangular component and the rotor is attached to a static gear around which it rotates. There are a ton of sealants used to makes sure that the entire operation remains air-tight. Because if there is either too much friction between the rotating components or less contact, this will result in loss of power due to lack of proper compression.
Also read: What are Variable Valve Timing and Lift? How do they affect performance and efficiency?
These are designed very carefully and since there are no reciprocating components, the vibrations are way too less. The operation is very smooth and the power delivery is also constant. This is because at each point of time during the operation, the intake, combustion and exhaust process are occurring simultaneously. This is the beauty of a rotary engine. Also, since it is not mounted vertically and there are no pistons, the centre of gravity of the car/engine is very low. Therefore, the handling and ride of the car are planted. These are way more compact than the inline or the V-type arrangements as well. The maintenance is low because of the low number of components overall. Here is a video to quickly make you understand the functioning of a rotary engine.
Also read: Types of Turbochargers – VGT, Twin-Turbo, Twin-Scroll, Sequential and E-Turbos!
We hope that this article has thrown some light on the types of engine arrangements out there and their purposes as well. We tried to explain the concepts in simple terms helping the technological understanding reach a wider audience. We hope you liked this article and do follow Car Blog India for more Automobile Technology-related content.
Image Source: Mechanical Engineering