In this edition of Automobile Technology Content, we have come up with a relevant and crucial aspect of the intake and exhaust processes of the IC Engines. As usual, the aim of these tech articles is to explain a complex and technical aspect of automobile engineering in a simple and easy-to-understand language. As we understand, there are plenty of automobile enthusiasts out there who are looking for such information as they want to know everything about their vehicles. So, let us get into this post without any further ado.
Also read: What are Front, Mid and Rear Engine Cars – Pros and Cons of each!
Purpose of Valves
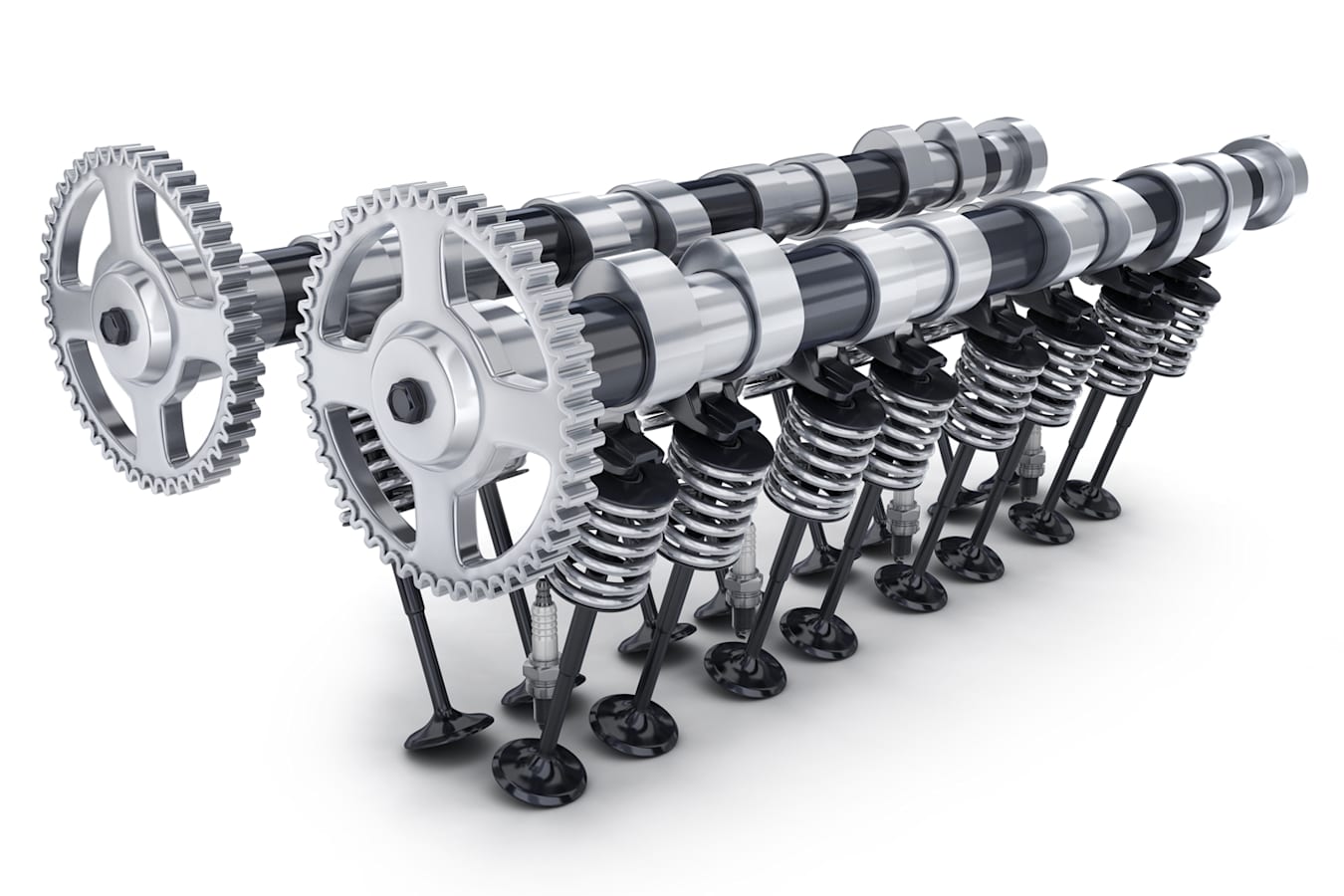
As many of you know already, the valves enable the breathing of the vehicles. Engines of the cars need fresh air to burn the fuel to generate power. Also, once the air is burnt, it needs to get released back into the atmosphere. This process is enabled or disabled by the valves inside the engine. When the engine needs air, they open up otherwise they ensure an air-tight compartment inside the engine. This is of utmost importance to ensure that the power that the engines produce doesn’t get compromised. To maintain the proper functioning of these valves, there are various mechanical components in place known as camshafts, cam lobes, rocker arms, springs, etc. This entire assembly constitutes the intake and exhaust strokes of the combustion cycle. During the power and compression strokes, these valves remain closed so that the entire power produced is utilized by the car and not wasted.
Also read: How safety features have evolved over the years in India automobile industry!
Single Over Head Cam (SOHC)
The components mentioned at the end of the last paragraph are arranged in a particular way which tells if what kind of system it is. For instance, if there is a single overhead cam to operate the intake and exhaust valves of the engine, it is known as a SOHC setup, as is also clear from the name itself. There are generally two kinds of scenarios associated with such kind of setup; two valves per cylinder or 4 valves per cylinder. All of these valves are managed by a single cam. The has pre-defined lobes on the shaft which push the rocker arm. This rocker arm pivots about the centre and in turn, presses the valve down. In this way, the valves open the intake/exhaust process. The springs attached to the valves ensure that the valves return to their initial position of rest after the intake/exhaust stroke has been completed. This is a relatively simple process with fewer components. Following are the advantages of SOHC.
Also read: What are the main components of a 4-stroke IC Engine – Pistons, Valves, Turbos, Camshafts & more!

Advantages and Disadvantages
- A simple process with fewer moving parts enables a simple construction and low weight overall.
- The manufacturing, repair and maintenance costs are relatively low.
- Less moving parts and forces to balance compared to the OHV (Over Head Valves) Setup.
- Good low-end torque and fuel economy because fewer parts consume energy.
- One of the downsides is the problem of the location of the spark plug because the centre space is occupied by the camshaft.
- Not too much control on the varying timing (VVT) or lift (VVL) of the valves.
Also read: Working of Synchronous and Induction Motors in (EVs) Electric Cars!
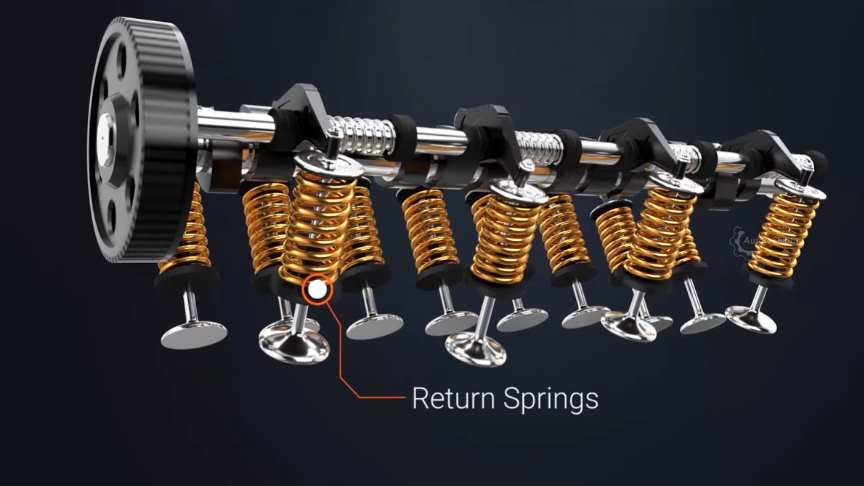
Double Over Head Cam (DOHC)
The more modern approach in the cars above the entry-level segment has the function of DOHC. As the name suggests, this setup incorporates a dual overhead camshaft setup to control and manage the valves. In such scenarios, one camshaft takes control of the intake process and the other of the exhaust process. Both can effectively work independently which offers a ton of flexibility in terms of various processes. The main point of difference between SOHC and DOHC is that there are no rocker arms in the DOHC process. The valves are operated directly via the camshafts without any rocker arm. General usage includes a 4 valve configuration; two for intake and two for exhaust cycle. There are plenty of advantages of using this type of setup and a few disadvantages as well, which we shall discuss now.
Also read: 6 Most Relevant Connected Car Tech Features in Modern Cars!
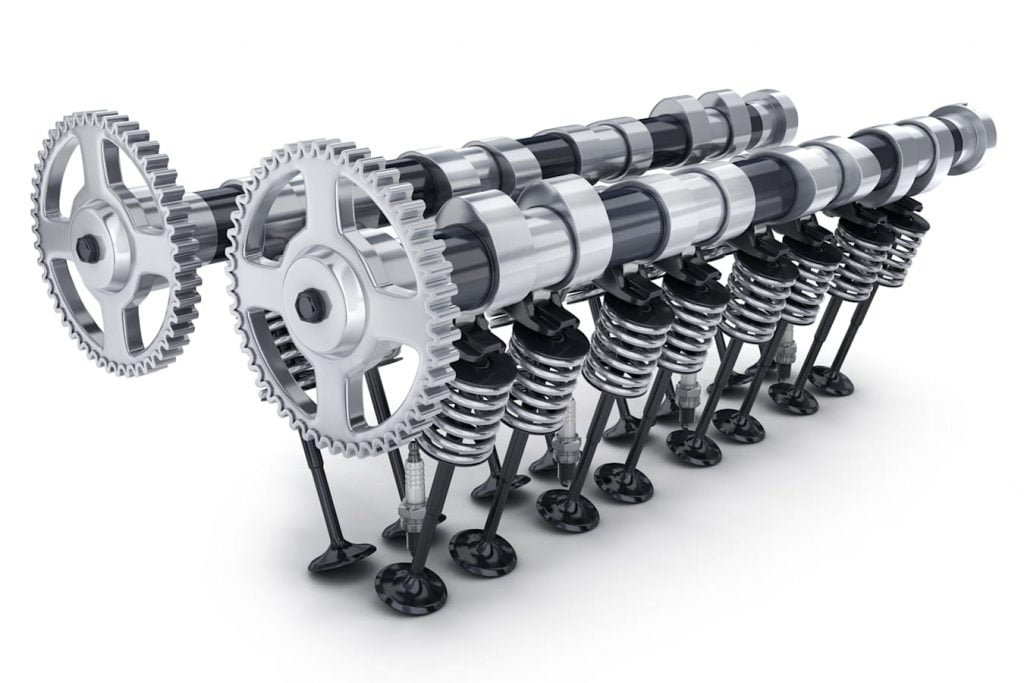

Advantages and Disadvantages
- Techniques like Variable Valve Timing (VVT) and Lift (VVL) can be introduced with the DOHC setup.
- This improves fuel efficiency as well as performance in terms of high RPM torque and power because of better airflow.
- Intake and Exhaust stroke cycles can be designed independent of each other according to the requirements of the engine.
- There is enough space to place the spark plug on the top and centre of the cylinder which is the ideal location for it.
- Few disadvantages include increased complexity which also increases the manufacturing costs.
- The overall weight of the system is increased due to the additional camshaft.
Also read: Working of Roots, Twin-Screw, Centrifugal Superchargers with Advantages!
Over Head Valves (OHV) or Pushrod
This is a unique design in the sense that the camshaft is located in the cylinder bank assembly. This is generally used with a V6 type configuration where the camshaft is placed in the V of the cylinder bank. This ensures a compact design assembly and construction. This is also known as Pushrod setup because the camshaft actually pushes the pushrods in these cases, which in turn, operate the rocker arms and eventually, the valves.
Also read: Working of Hydraulic, Electric and Electrohydraulic Power Steerings!
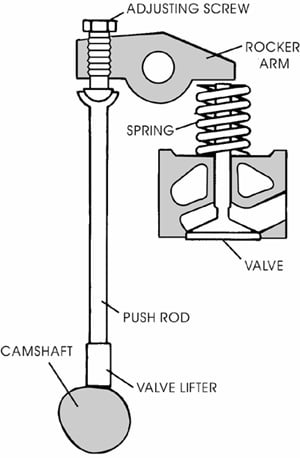
Advantages and Disadvantages
- Compact construction enabling better packing efficiency of the engine.
- It is a bit less complex compared to the DOHC setup which also means that it is a bit cheaper to manufacture.
- Because of the usage of a pushrod, the number of valves per cylinder is generally limited to two.
Also read: What is Air Suspension – Uses of Soft and Stiff Springs!
We hope you enjoyed this edition of our Automobile Technology Section. If you are interested in more such posts, head to Car Blog India and Automobile Technology where you can find such intriguing technologies in simple language.
Also read: What are Catalytic Converters and how do they reduce emissions?
Image Source: Pak Wheels , Sia Magazin , Whichcar