A brief explanation of the 48-volt mild hybrid system
By definition, a hybrid vehicle is a form of transportation propelled by two or more separate systems which can either work separately or in conjunction with each other. But that is something most people already know and are familiar with. What has got everyone talking now, however, is the ‘mild hybrid’ technology that is currently being employed by Maruti Suzuki in the diesel variants of the Ciaz and the Ertiga. This technology is not as complicated as the one employed by more conventional hybrids like the Toyota Prius and Camry, but it is cheaper and very effective. According to Delphi, vehicles with 48-Volt systems have demonstrated 70 percent of the benefit at 30 percent of the cost. In order to help you better understand the science behind this Delphi 48-Volt Mild Hybrid System we shall attempt to explain the same with the help of a few infographics courtesy Delphi Automotive.
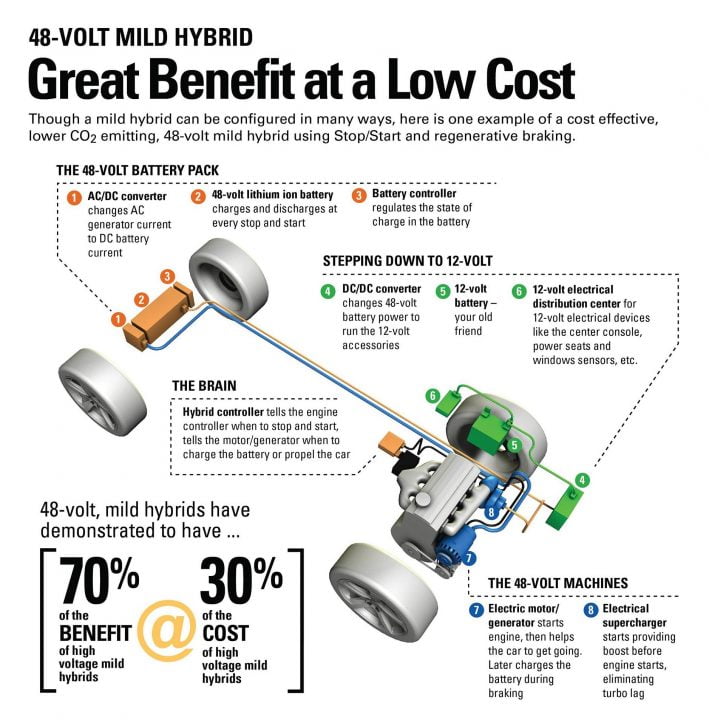
A 48-Volt Mild Hybrid setup can have multiple layouts. One such possibility is shown here in the picture. The major additional components here are the bigger 48-Volt battery pack, step down converter, electric motor/generator and electrical supercharger.
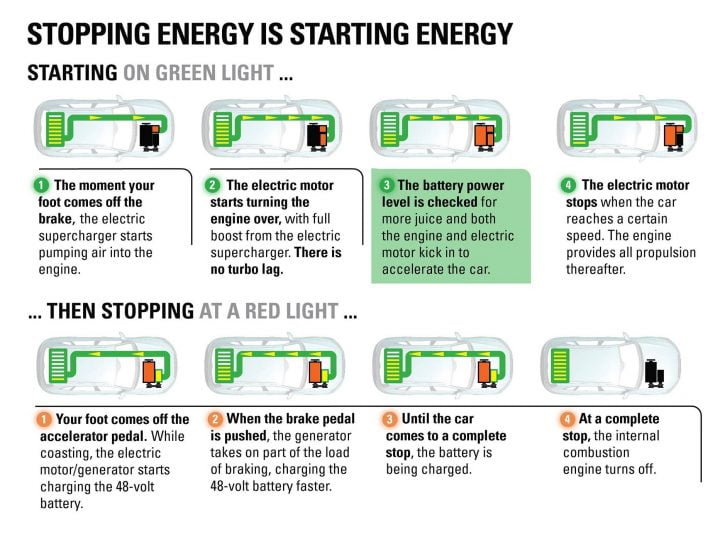
The electric supercharger comes into action upon releasing the brake as it starts forcing air into the engine. This helps negate the turbo lag usually associated with engines that employ turbochargers. The electric motor powered by the battery packs assists during acceleration and automatically cuts off after reaching a certain speed.
Mild Hybrids come coupled with engine start/stop systems. This system turns off the motor once the car comes to a complete stop and turns it back on again once the clutch pedal is pressed. Before the car comes to a complete rest, during the time the driver’s foot is off the accelerator when the car is coasting the electric motor charges the 48-volt battery pack.
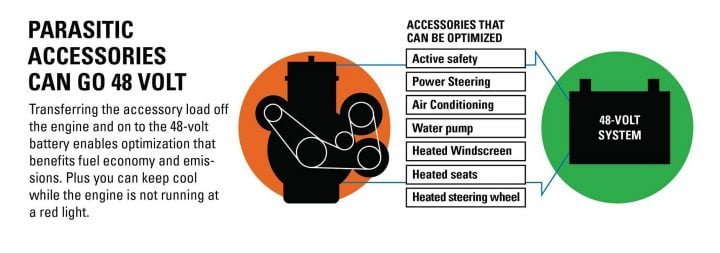
Another application of having a bigger battery pack, such as a 48-volt setup, is that some of the load borne by the engine due to parasitic accessories such as the power steering, AC, water pump, heated seats, etc. can be transferred to it. Also, the air conditioning will not turn off when the engine does as it will draw power from the battery.
According to Delphi Automotive, “48-Volt mild hybrids, for gasoline or diesel engines, could reduce the percentage of CO2emissions by double digits, capture energy typically lost while braking and provide torque in the low rpm range for anemic start-stop hybrids. The beauty of a 48-Volt solution is that drivers will not lose engine performance to gain fuel efficiency from downsized engines. Consumers would drive these 48-Volt cars the same way they would drive cars powered by conventional powertrains, and they would enjoy the 20 percent extra horsepower the 48-Volt system provides.”
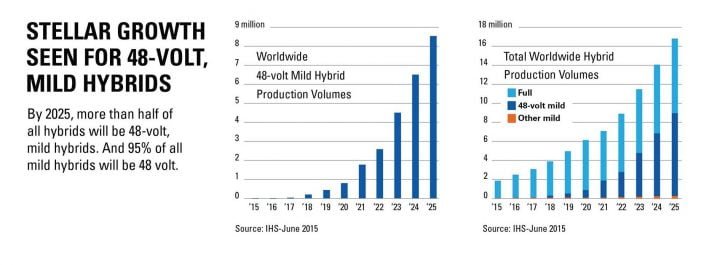
By 2025, 48-Volt hybrids are expected to make up more than 95 percent of the world’s mild hybrid market and about half of all hybrid vehicles, according to Global Insight IHS.
We hope you found this post on the Delphi 48-Volt Mild Hybrid System informative and insightful. Stay tuned to Car Blog India for more such features.